
This can happen if there is a natural or human-made disaster, like a hurricane destroying a factory and machinery. Furthermore, an inward shift is also possible. And if this country wants to increase the production of clothes from 100 to 150 units, they must sacrifice the production of 25 units of food.Īn outward shift of the production possibilities frontier is only possible if the country discovers new resources or there is an improvement in technological development. If this country wants to increase the production of food from 50 to 75 units, this requires sacrificing the production of 50 units of clothes. The graph above demonstrates this trade-off. The government must assess the opportunity cost of producing more of one or the other. Likewise, if they want to produce more clothes, they must produce less food. If the country wants to produce more food, they must produce fewer clothes, based on limited resource availability. F shows an unattainable level of production, based on current resources.a case in which the output is less than what it has the potential to be


Economists do this in order to isolate a particular relationship, so that other variables do not obscure what they’re attempting to discover. One of the first and most important things to note is that economists often base their models off of key assumptions such as “ ceteris paribus,” meaning all else remains the same or all other variables are kept constant. Similar Posts: Production Possibility Frontier Assumptions This allows the country’s limited resources to be allocated most efficiently and completely. Meanwhile, within the field of macroeconomics, it’s production possibilities frontier shows the situation in which a company is producing goods/services most efficiently to use resources the best possible way, in light of limited production capabilities. Within business analysis, the production possibility curve represents the various production levels of two goods requiring one resource that is available in a limited amount.
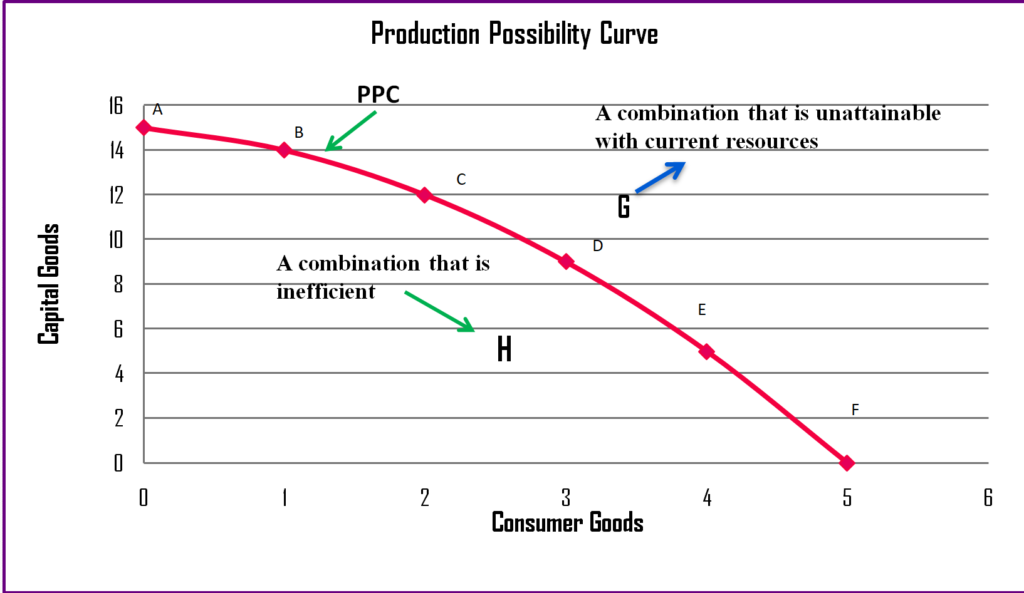
The production possibilities frontier is a concept in the fields of both business analysis and macroeconomics. Economists use PPF to illustrate the trade-offs that arise from scarcity. Selecting one alternative over another one is known as opportunity cost. A production possibility curve even shows the basic economic problem of a country having limited resources, facing opportunity costs and scarcity in the economy. The production possibilities frontier shows the productive capabilities of a country. Be aware that the “production possibilities curve” (PPC) is another way of referring to the production possibilities frontier, referring to the curve shown on a graph of the frontier-see below for an example of such a graph. The best way to show a country’s available resources, along with the maximum two goods produced from those resources, is by calculating the production possibilities frontier (PPF).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
